What Are the Symptoms of Ringworm?
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but by a fungal infection. This common infection affects the skin, scalp, and nails and appears as a red, ring-shaped rash. Ringworm can affect people of all ages and is especially contagious. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage and prevent its spread effectively.
What Causes Ringworm?: Symptoms of Ringworm
Ringworm is caused by a type of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments. The infection can be spread in several ways:
- Person-to-Person Contact: Ringworm spreads easily through skin-to-skin contact with someone who has the infection.
- Animal-to-Human Contact: Some animals, especially pets like cats and dogs, can carry ringworm and transmit it to humans.
- Object-to-Human Contact: Fungi can live on surfaces, including clothes, towels, bedding, and personal items, for a while. Sharing these items with an infected person can lead to ringworm.
- Environmental Exposure: Warm, damp places like locker rooms, pools, or shared gym equipment can harbor the fungi, making it easy to pick up the infection from these places.
Who is Most at Risk of Ringworm?
Anyone can get ringworm, but certain groups may be at higher risk:
- Children: They often catch it through close contact at school or during play.
- Athletes: Wrestlers and other athletes in close-contact sports can easily catch ringworm.
- People with Weak Immune Systems: Those with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to severe ringworm infections.
- Individuals in Warm, Humid Climates: The fungus thrives in warm and humid areas, making people in such climates more vulnerable.
Common Symptoms of Ringworm
Ringworm symptoms vary depending on the affected area of the body. Here’s a breakdown of symptoms based on the location:
- Skin (Body) Ringworm:
- A red, itchy, ring-shaped rash with a defined, raised edge.
- The rash may be scaly and cause peeling or cracking.
- It commonly appears on exposed areas like the arms, legs, and torso.
- Scalp Ringworm (Tinea Capitis):
- Round, scaly bald patches on the scalp that may feel tender.
- Itching and soreness around the affected area.
- Hair loss in patches as the infection spreads.
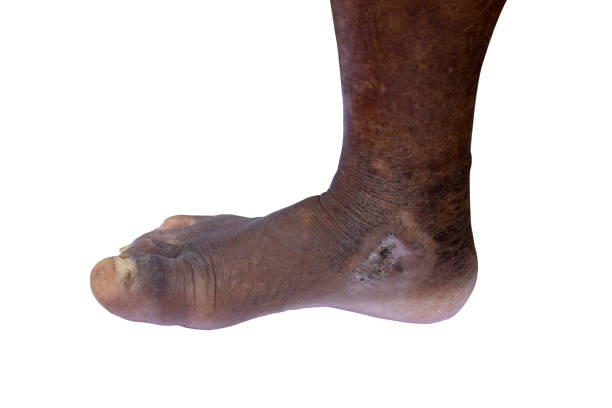
- Foot Ringworm (Athlete’s Foot or Tinea Pedis):
- Red, scaly, and cracked skin between the toes.
- Burning or itching sensations, especially after taking off shoes.
- Blisters may appear and lead to oozing if not treated.
- Nail Ringworm (Onychomycosis or Tinea Unguium):
- Thickened, discolored nails, often turning yellow or white.
- Brittle or crumbly nails that may separate from the nail bed.
- The infection usually starts at the tip of the nail and spreads deeper.
Treating and Preventing Ringworm
Treatment: Most cases of ringworm can be treated with antifungal creams, sprays, or lotions. Your doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal medication if the infection is extensive. Treatment options may include:
- Topical Antifungal Creams: These are effective for mild cases of ringworm on the skin and athlete’s foot.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: In cases of scalp ringworm or nail infections, your doctor may recommend oral antifungal drugs.
Prevention:
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Fungi thrive in warm, damp environments, so make sure to dry off well after swimming or bathing.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Don’t share towels, combs, or clothing with others, especially if they have an active infection.
- Wear Sandals in Public Areas: To avoid athlete’s foot, wear sandals in locker rooms, public showers, and around pools.
- Wash Hands Regularly: Washing hands after touching pets or surfaces that may be contaminated helps prevent spreading the infection.
If you suspect you have ringworm and over-the-counter treatments haven’t worked, or if the infection appears to be worsening, it’s time to seek medical advice. For personalized care, consult a doctor on the Virtual Doctors App or download the Virtual Doctors Healthplus App on Google Play. Professional medical advice ensures that you get the appropriate treatment, especially for severe or stubborn infections.
Ringworm is a common, highly contagious fungal infection, and although it’s uncomfortable, it’s treatable. Recognizing the symptoms early and taking preventive measures can help stop the spread of ringworm. For cases that are persistent or severe, consult a healthcare provider through the Virtual Doctors App. By following the steps above, you can effectively manage and prevent this common skin infection.