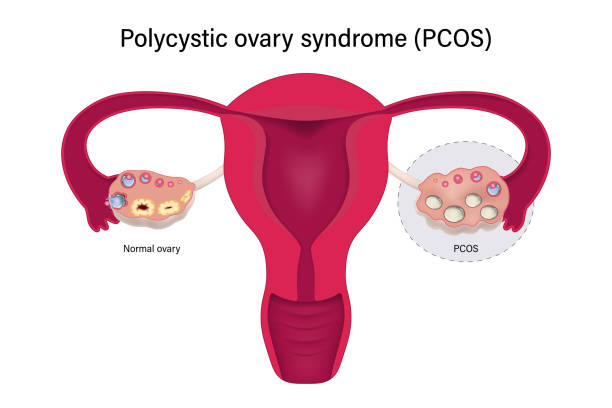
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. Characterized by irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, and small cysts on the ovaries, PCOS can impact a woman’s overall health and fertility. Understanding symptoms of PCOS and causes is essential for early diagnosis and management.
What Causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is unclear, but several factors are believed to play a role:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Women with PCOS have higher levels of androgens, often called “male hormones.” This hormonal imbalance can interfere with ovulation and lead to symptoms like excessive hair growth and acne.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which means their bodies do not use insulin effectively. This leads to higher insulin levels, which may cause the ovaries to produce more androgens.
- Genetics: PCOS often runs in families. If your mother, sister, or other female relatives have PCOS, your risk of developing the condition may be higher.
- Low-Grade Inflammation: Women with PCOS may have low-grade inflammation, which can contribute to increased androgen production and other symptoms.
What Are the Common Symptoms of PCOS?
Symptoms of PCOS vary among individuals. While some women may have mild symptoms, others experience more severe signs. Here are the most common symptoms:
- Irregular Periods
- Fewer than nine periods a year.
- Long gaps between periods (more than 35 days).
- Heavy bleeding during periods.
- Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism)
- Unwanted hair on the face, chest, back, or other areas typically more common in men.
- Acne and Oily Skin
- Persistent acne on the face, chest, or back, caused by high androgen levels.
- Thinning Hair or Hair Loss
- Hair thinning or bald patches on the scalp similar to male-pattern baldness.
- Weight Gain
- Unexplained weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, is common in women with PCOS.
- Darkened Skin Patches
- Dark, velvety patches of skin, particularly around the neck, groin, or under the breasts, can occur due to insulin resistance.
- Fertility Problems
- Difficulty getting pregnant due to irregular ovulation or no ovulation at all.
- Mood Swings and Fatigue
- Depression, anxiety, and fatigue are also common symptoms of PCOS.
What Are the Long-Term Risks of PCOS?
If left untreated, PCOS can increase the risk of developing other health issues, including:
- Type 2 diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- Heart disease.
- Sleep apnea.
- Endometrial cancer.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce these risks and improve overall health.
How Is PCOS Diagnosed?
PCOS is typically diagnosed based on:
- A review of your symptoms and medical history.
- A physical examination.
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels.
- An ultrasound to check for ovarian cysts and measure the thickness of the uterine lining.
Treatment Options for PCOS
While there’s no cure for PCOS, its symptoms can be managed effectively with the right treatment. Here are some common treatment approaches:
- Lifestyle Changes
- Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise can help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate periods.
- Medications
- Birth Control Pills: Help regulate periods, reduce androgen levels, and control acne.
- Metformin: Improves insulin resistance and can help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Anti-Androgen Medications: Reduce excess hair growth and acne.
- Fertility Treatments
- If you’re trying to conceive, medications like clomiphene or letrozole can help induce ovulation.
- Hair Removal and Skin Treatments
- Options like laser therapy or topical creams can help manage excess hair growth and acne.
When to Seek Medical Help: Symptoms of PCOS
If you notice symptoms of PCOS, such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth, or difficulty conceiving, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and guidance.
For personalized advice and effective treatment, connect with qualified medical doctors on the Virtual Doctors App.
PCOS is a manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated appropriately. Understanding the symptoms and working with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan can help reduce its impact on your daily life and long-term health. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help for PCOS management and improve your quality of life today.