Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is a chronic infectious disease that has affected humanity for thousands of years. Although it’s rare today and curable with timely treatment, it’s important to be aware of the symptoms and causes to seek early intervention. This article explains the causes, symptoms, and necessary steps to take if you suspect leprosy.
What is Leprosy?: Symptoms of Leprosy
Leprosy is caused by a slow-growing bacterium known as Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin, nerves, eyes, and the lining of the nose (nasal mucosa). Contrary to old beliefs, leprosy is not highly contagious, and it requires prolonged, close contact with someone who has untreated leprosy to spread.
While leprosy is often associated with historical stigma, modern medicine has made the disease fully treatable, and most people who receive early treatment do not develop disabilities. Leprosy is classified into different types based on the number and kind of skin sores or lesions a person has.
Causes of Leprosy: Symptoms of Leprosy
Leprosy is transmitted via droplets from the nose and mouth of untreated individuals with severe infections. The bacteria spread through prolonged contact with an infected person, such as living in the same household. However, many people who come into contact with the bacteria do not develop the disease due to their immune system’s ability to fight off the infection.
While anyone can contract leprosy, the disease is more common in areas with poor sanitation and limited access to medical care. People living in regions like Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America are at a higher risk. Genetics also play a role, as some people are more susceptible to the bacteria.
Symptoms of Leprosy
The symptoms of leprosy can take a long time to appear, sometimes between 1 to 20 years after exposure to the bacteria. The disease progresses slowly, which is why early symptoms can be difficult to recognize. Below are the common symptoms of leprosy:
1. Skin Lesions
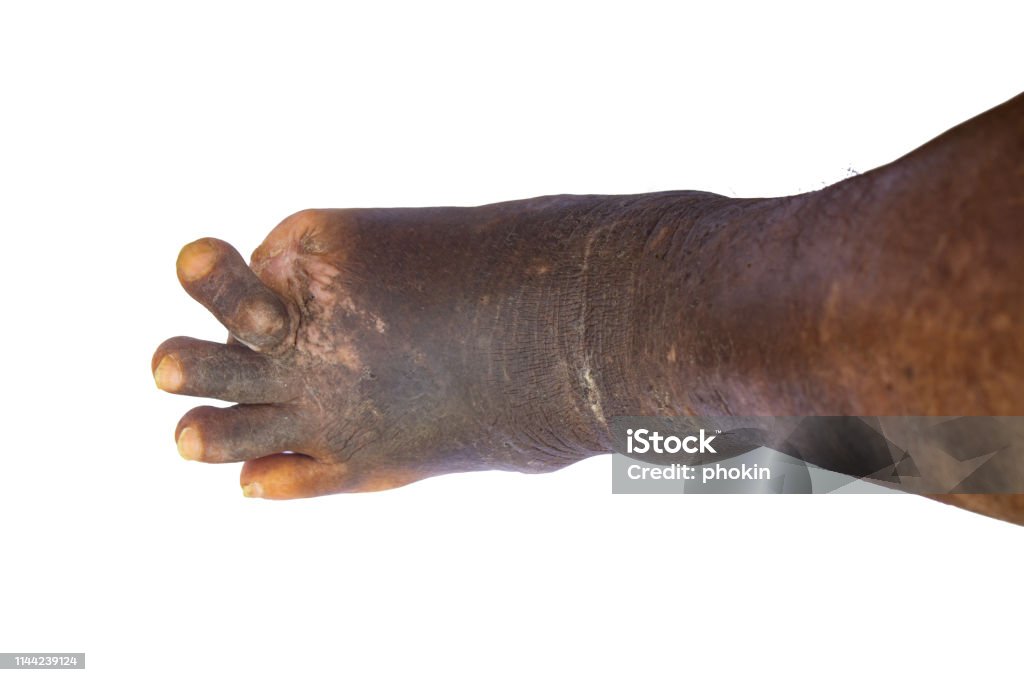
The most noticeable and common symptom of leprosy is the appearance of pale or reddish skin lesions or patches that may lose sensation. These patches usually don’t heal on their own and can become numb to touch, heat, or pain due to nerve damage.
2. Numbness in Hands, Feet, and Extremities
Leprosy damages the peripheral nerves, leading to numbness or a tingling sensation in the hands, feet, arms, and legs. As the disease progresses, individuals may lose the ability to sense pain in the affected areas.
3. Muscle Weakness
Leprosy can cause muscle weakness, particularly in the hands and feet. People with untreated leprosy may struggle with everyday tasks, such as gripping objects or walking, due to the weakening of muscles.
4. Eye Problems
Leprosy can affect the eyes, leading to problems such as dryness or difficulty blinking. In severe cases, untreated leprosy may result in blindness if the bacteria damage the nerves around the eyes.
5. Ulcers on the Soles of the Feet
Due to the numbness caused by nerve damage, people with leprosy may develop ulcers on their feet. These ulcers occur because injuries or wounds on the feet may go unnoticed and untreated.
6. Enlarged Nerves
Nerve damage caused by leprosy can lead to visibly enlarged nerves, especially in areas such as the elbows, knees, and sides of the neck. These enlarged nerves can sometimes be tender or painful.
7. Nosebleeds and Nasal Congestion
In some cases, leprosy may affect the nasal passages, leading to symptoms like a stuffy nose or nosebleeds. This is due to the bacteria attacking the mucous membranes of the nose.
What Should You Do if You Suspect Leprosy?
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, especially persistent skin patches or numbness in your hands or feet, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent long-term damage to your nerves, skin, and other organs.
You can get professional medical help by consulting a doctor through the Virtual Doctors App, or you can download the Virtual Doctors Healthplus App on Google Play to book an appointment with a qualified doctor.
Treatment for Leprosy
Leprosy is treatable, and early detection is key to preventing complications. The standard treatment is known as multidrug therapy (MDT), which involves a combination of antibiotics taken over a period of 6 to 12 months, depending on the severity of the infection. MDT effectively kills the bacteria and stops the disease from progressing, ensuring the patient is no longer contagious.
Once treatment begins, the person becomes non-infectious within a few days, and further transmission of the disease is prevented. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment to fully eradicate the infection.
Preventive Measures
To prevent leprosy, the most important step is early detection and treatment of infected individuals to stop the disease from spreading. Other preventive measures include:
- Avoiding prolonged contact with untreated individuals who have leprosy.
- Good hygiene practices to reduce the risk of infection.
- Regular medical checkups, especially for those living in high-risk areas.
Leprosy is a serious but treatable condition, and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for early intervention. If you or someone you know is showing signs of leprosy, it’s important to seek medical care immediately. You can book a consultation with a doctor using the Virtual Doctors App or download the Virtual Doctors Healthplus App for quick access to qualified healthcare professionals.